How Important Is Journey Mapping Nowadays for All Businesses?
The business landscape is highly competitive nowadays. Therefore, understanding and meeting customer expectations is paramount for success. Customers have become more discerning and demanding, and online businesses must go with a more personalised approach to gain a competitive edge. The great news is that we have tools to understand better our target audience, its needs, expectations and goals. One of these tools is journey mapping which enhances customer understating, improves their experience, aligns business processes, drives innovation and differentiation, and facilitates continuous improvement.
In this article, we will explore what journey mapping is, what components to consider, its importance, and how to create a journey map to enhance your business growth further, boost customer satisfaction and loyalty. Follow along for valuable knowledge and inspiration that can help you offer exceptional customer experiences.
What is Journey Mapping?
Customer journey mapping can be described as a visual representation of various touchpoints an online visitor encounters while engaging with your website. By mapping out this journey, you get a holistic view of the customer experience, identify pain points and moments of delight, and areas for improvement. This action goes beyond isolated interactions and takes into consideration the whole end-to-end experience, from the first point of contact through post-purchase support.
The customer journey mapping process enables businesses to create a holistic strategy and approach to customer experience management and ensure that all customer touchpoints are optimised to deliver fantastic user experiences. It provides a relevant perspective into consumers’ emotions, needs, and expectations at different journey stages. These insights will help you make informed and data-driven decisions to enhance customer satisfaction further, build loyalty and drive business growth. Furthermore, the mapping process will empower your company to align your strategies, processes, and resources with the user’s journey, resulting in improved experience and increased customer loyalty.
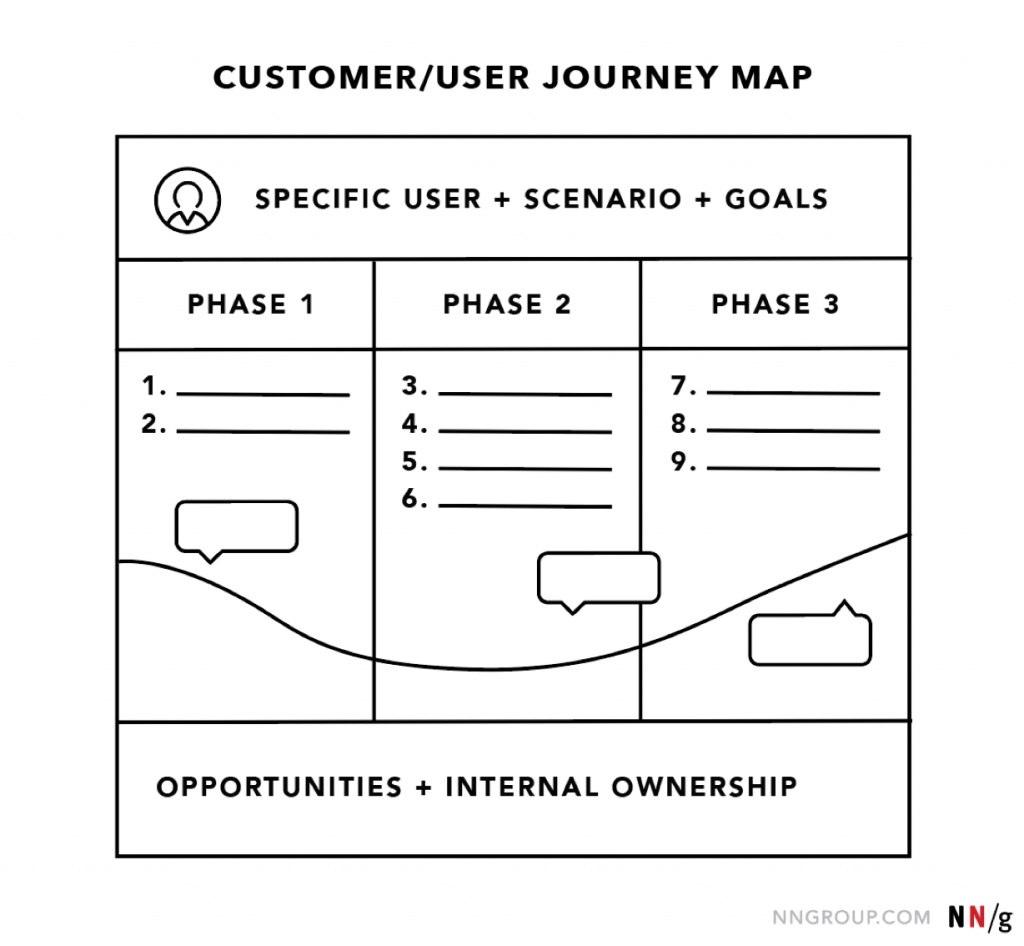
Journey Map Components
Customer journey maps comprise various components that work together to offer a comprehensive understanding of the customer experience. These components aid businesses in discerning key touchpoints, pain points, bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement throughout the customer journey. Let’s explore together the key elements of a customer journey map:
- Buyer persona or customer persona – one of the essential components is the customer persona or buyer persona, which represents the ideal customer and their characteristics, preferences, and goals. The customer personas and their actions in the journey map are rooted in data. However, we strongly encourage you to build solid and clear narratives. Each persona has a point of view and will experience the journey differently based on the user type (ex., a business will have a distinct point of view and user journey than a regular website visitor, or a loyal customer will have a different perspective about your brand than a first-timer). By incorporating various customer personas into the journey map, businesses can personalise the user experience and tailor it to accommodate and satisfy specific customer segments or customer profiles.
- Customer journey timeline – the timeline or timeline axis represents the chronological order of touchpoints and customer interactions. This component allows businesses to visualise the sequence of events and identify the duration and repetitiveness of each touchpoint. We recommend creating scenarios and expectations. Describe the situation that the journey map discusses and link a buyer persona’s goal, expectations and needs. You can create realistic scenarios for existing products or services by involving events such as purchasing, downloading an ebook, or planning an itinerary for a future trip. We advise you to describe the whole process in detail and include various communication channels and transitions. The timeline axis provides insights into the user’s journey progression and the overall timeline of the experience.
- Touchpoints or journey phases – each point of interaction between a user and a business are also detrimental to a journey map. These touchpoints can occur across various channels, such as a website or mobile app, social media platforms or physical locations. Every touch touchpoint represents an opportunity for companies to engage with their customers and leave a lasting impression. The journey phases provide a better organisation for the remaining components of a map. The touchpoints or phases will vary based on the scenario and the business industry. A potential scenario for an eCommerce business consists of five stages: discovery, try, purchase, use and asking for support. For an important purchase such as buying a house, the journey phases can start with customer engagement, followed by education, research, evaluation and justification. Suppose you have a B2B business model. In that case, the stages can be purchasing your product or service, adoption of your service or product by the buyer, customer retention, expansion of your product or service, and advocacy by the client to other businesses. By identifying and analysing each touchpoint, you can assess the quality of the interaction and optimise them to enhance the entire customer journey and experience.
- Customer actions, emotions and expectations – a user journey map must include the customer’s emotional journey, as this component will give you a better understanding of a user’s emotional highs and lows of the experience. Customer actions refer to the user’s behaviour, and you can record every step of their interaction. The emotions or the mindset describes a user’s motivation, thoughts and questions during each phase of the journey. By capturing the emotional state at each touchpoint, you can identify pain points and bottlenecks that generate confusion, dissatisfaction, frustration or distrust. Conversely, moments of delight can be identified and leveraged to create memorable experiences that foster loyalty and advocacy.
- Supporting data and metrics to identify opportunities – this stage of the map will provide a quantitative perspective. You can analyse metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, conversion rates, customer feedback, time on site, etc. We strongly encourage you to integrate data and metrics into your marketing strategy to measure the effectiveness of customer journey touchpoints, identify areas for improvement, and track the impact of changes made to the customer experience. We also advise adding qualitative insights, such as customer feedback, reviews and testimonials, to add a human touch to the analysis. These insights offer more depth and context to the journey, helping you understand the underlying motivations, needs and bottlenecks expected by users.
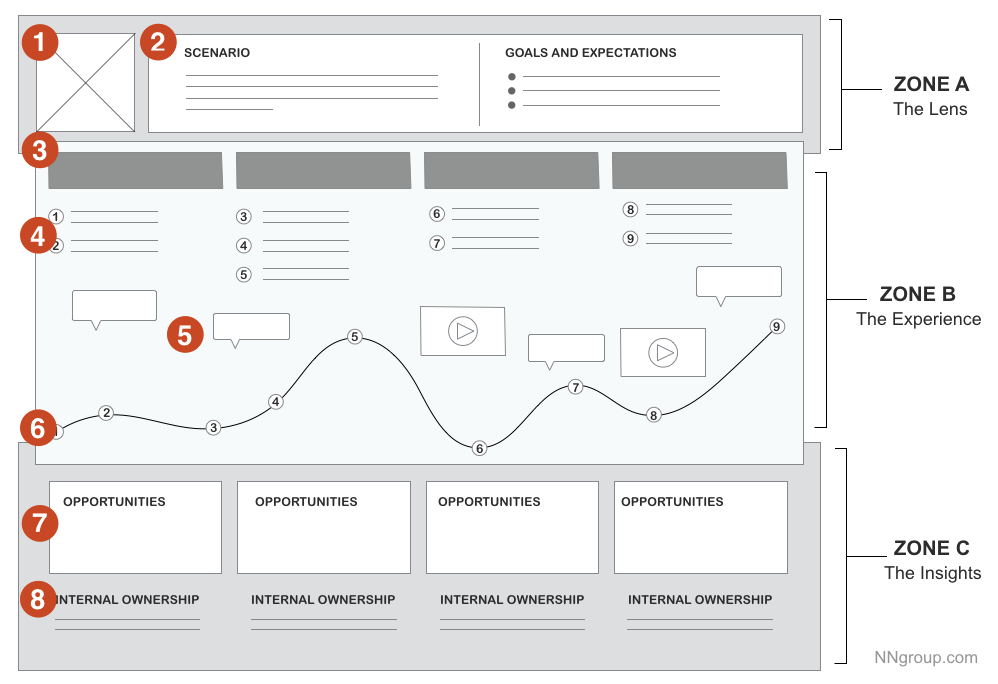
The components of a journey map are designed to work in harmony to create a visual representation of the customer experience and offer your business a holistic understanding of the entire customer journey. This comprehensive view enables companies to identify areas for improvement, prioritise initiatives, and design targeted strategies to deliver fantastic experiences in every phase of the journey and reach business goals faster.
The 5 E’s in the Customer Journey
The 5 E’s in the customer journey refer to the different stages or phases consumers go through when interacting with a product, service, or company. These stages are often analysed to understand the user experience better. The 5 E’s are as follows:
- Entice: This is the stage where you focus on grabbing a user’s attention and generating initial interest. This involves marketing efforts, social media, advertising, content, and other tactics to engage potential customers and encourage them to learn more about your offers.
- Enter: This stage is where consumers take their first step to engage with your business and initiate the first connection. This could involve various actions based on your offer. It could be visiting a physical store, landing on your landing page, downloading an app, filling out a form, etc.
- Engage: This stage is where the users actively interact with the product, service, or company. They can explore, learn and experience what you have to offer. This stage is crucial for building engagement and establishing a positive user experience.
- Exit: This stage occurs when consumers complete their interaction or transaction. It involves the conclusion of the engagement, like completing the purchasing process, ending a service, or leaving a website. In this stage, you have the opportunity to leave a lasting positive impression on the user.
- Extend: This stage focuses on fostering an ongoing relationship with the customers beyond the initial engagement. It involves strategies to retain customers, encourage them to repeat purchases and promote loyalty. In this stage, we recommend including customer loyalty programs, personalised recommendations and ongoing support.
The 5 E’s provide a framework to analyse and map the customer journey, helping businesses understand the various stages and touchpoints consumers go through. Each stage must be understood in detail to further optimise your strategies and efforts to enhance the overall customer experience, drive customer satisfaction, and foster long-term loyalty.
How Important Is Journey Mapping Nowadays for All Businesses?
We consider user journey mapping mandatory action in today’s business landscape. As customers have a plethora of options at their fingertips and are more willing than ever to switch brands if their expectations are unmet, companies must deliver personalised and optimised types of customer journeys to gain a distinct advantage.
You might consider that journey mapping might not be a must-have in your company, but understanding the needs and bottlenecks of your customers is essential in a user-centric business. If your business mentality is all about helping your consumers, solving their problems and achieving long-term success, then aligning each journey phase with a business goal and optimising each touchpoint accordingly, you are heading to maximising customer success.
- Journey mapping can be used to repurpose your marketing and business strategy with an inbound perspective. You can focus on creating content and promotional materials based on what your consumers already want. You can catch their attention first and focus on sales second. The inbound perspective will give you valuable information about what your audience wants and what drives them away. Therefore, when you work with data-driven information, you grab their attention and keep them engaged for longer times.
- You can discover and create a new target customer base based on demographics, behaviours and psychographics. Instead of focusing your efforts on attracting a broad audience, you can grab the attention of the people who are interested in your brand, products or services. Your business goals can be achieved more easily when you can address the needs and pain points of your regular consumers.
- You can better your customer service. As a journey map is a roadmap to the user’s experience, you can learn when they are delighted and where are the moments they experience friction and frustration. By identifying these elements, you can adapt your customer service strategy and take action at ideal times. Your customer service team can proactively increase your brand’s trust, especially when a customer service surge can happen. We strongly recommend you inform your audience of any changes in your team schedule for special events such as holiday hours and tell them about other support options available. You can implement AI-powered chatbots to address the most common questions if your clients need fast solutions.
- You can enhance retention rates. When you have a deeper understanding of your target persona and their journey, it is easier to identify and address common customer pain points quickly. By doing so, fewer people will go to your competitors, as 32% of consumers will stop doing business with a brand they love after only one bad experience. An effective user journey map can highlight the individuals that might be on the way to churn, and you can identify these behaviours and start engaging them before leaving your website. It is essential to keep in mind that you cannot save all of them.
- You can build a customer-centric product strategy and customer-focused mentality in your company. Aligning your sales teams, marketing departments, customer support team, etc., can be difficult as your company grows, but sharing an accurate customer journey map with all departments will provide a clearer understanding of each step of the buyer journey, from the initial engagement of potential customers to post-purchase support.
Types of User Journey Map Variations
A user journey map can have several variations that address various points of the customer relationship with your brand. We want to underline the definitions of these variations to guide you to the most fitted method for your company.
- Experience Map – an experience map is a holistic overview of general human behaviour. This variation identifies each and every step of an average customer and provides a complete end-to-end user experience to achieve a goal.
- Service Blueprint – a service blueprint is a visualisation of the relationship between various service delivery by detailing all the activities that occur in each phase and are performed by different people involved in these processes. This variation is an extension of the journey map that, instead of focusing on the customer perspective, is focused on your business.
- User Story Map – user story maps are used in the Agile methodologies to design features or software functionalities. Each feature and functionality is described from a user’s point of view, and it focuses on what a consumer would like to do and how this functionality or feature will help them achieve their goal.
As you can observe, these user journey map variations are used at a specific point in the process. Think of these as small puzzle pieces of a journey map. While you can take advantage of these variations, keep in mind that only a holistic journey map can offer you a deeper understanding of the user’s pain points, emotions and actions.
Our Advice – How To Create a Journey Map?
In this chapter, we will guide you on creating a journey map to maximise your business revenue, enhance the current experience and strengthen the relationship with existing clients, engage your target user and attract prospective customers.
- The first step is to ensure that each key component of your map is clear, researched and based on truthful narratives of real customers.
- Next, you should define the purpose and scope. We advise you to start your customer journey design map by determining specific objectives. Ensure that your “why” and “what” have clear answers and you stay focused on relevant details. Determine what is the goal of this map. Are you focusing on a specific customer segment or a particular product or service? Who will use the product or service? What kind of experience will this map address, and for whom? How will I share this map, and on what social channels?
- Identify user personas that represent the different types of customers you interact with. These personas should encompass key characteristics, goals, needs, and pain points of your target audience.
- Map out the stages by identifying key stages of the user journey, such as awareness, research, purchase, onboarding, usage and support. We recommend tailoring these stages to align with your specific business and customer journey.
- Capture touchpoints at each stage of the journey. The touchpoints are key interactions or points of contact between potential customers and your business. Remember that these touchpoints can be online and offline, such as website visits, social media interactions, phone calls, messages, or in-store visits.
- Gather customer insights by collecting feedback through customer interviews, reviews, focus groups, or surveys. This qualitative data provides valuable information about consumers’ emotions, motivations, pain points, and expectations at each touchpoint.
- Create a visual representation of the customer journey map. We recommend creating a visual representation of the journey map using a simple diagram or flowchart or a more sophisticated customer journey mapping tool such as Smaply. We also recommend using customer journey map templates. HubSpot has a great collection of templates that can help you underline stages and touchpoints, create user personas and connect them in a logical flow.
- Incorporate emotional and behavioural aspects of consumers at each stage and when they reach a touchpoint. Highlight their emotions, needs and actions, such as delight, pain points, and areas for improvement. This aspect will humanise the journey map and provide a deeper understanding of the user experience.
We want to emphasise that journey mapping is a repetitive process because consumers’ needs and the market dynamics are changing continuously. We strongly recommend regularly updating, refining and validating your journey map to keep it relevant and effective.
We would also like to give you some extra tips to ensure your efforts are pointed in the right direction, and you stay on track while working on the user journey map.
- Ensure that your maps are based on truthful narratives. Gather all the research to understand the existing experience and identify the gaps that this research does not cover. This type of qualitative data will provide support and also validate your hypothesis.
- Validate and refine your journey map with stakeholders, team members, and consumers. This will increase accuracy and effectiveness.
- Take your time with the visualisation process until you ensure your data is complete and precise. Rushing this process can lead to flawed journey maps.
- Once created, make sure you use the journey map because it is a valuable tool for decision-making and improvements. This will help you identify pain points, prioritise enhancements and align business processes to deliver a better customer experience.
By following these steps, you can create a journey map that provides a holistic view of the customer experience and guides your efforts in delivering exceptional experiences at every touchpoint. We can help you achieve success with the right digital marketing techniques. Contact us today!
Businesses of all sizes and industries should use customer journey maps. Departments like the marketing team, customer experience teams, product development teams, sales teams, customer support teams and the executive leadership benefit from using a journey map.
Customer journey mapping is valuable because you will understand the customer experience, identify pain points and opportunities, enhance customer-centricity, align touchpoints and channels, drive improvements and innovation, and foster cross-functional collaboration.
A customer journey map has no fixed number of steps because it varies based on complexity and specific needs. However, we recommend including all the stages that reflect key touchpoints and interactions and focus on capturing the customer’s progression, actions, emotions and touchpoints.
A customer journey stage is a specific step or phase where the user progresses through various interactions, touchpoints, and emotions as they move towards achieving their goals or fulfilling their needs.