What Is the Difference Between UI and UX Design?
It is easier than ever to build a website right now, but in a highly competitive market and a fast-paced environment, your website must stand out from the crowd. If you wonder what makes a good website, we have the answer for you: custom development, outstanding UX and UI design, implementation of website performance optimization solutions, a rock-solid SEO and digital marketing strategy.
In today’s article, we are going to focus on the visual design of a website. We have noticed during the years that UX and UI are the two most often confused terms in web and app design. Usually are placed together as such UX/UI design, and viewed from a superficial point of view, they seem to describe the same thing. But, we are here to show you the differences between user experience design (UX) and user interface design (UI), how they work together, and why you might consider giving them a bit more attention.
What Is User Interface (UI) Design?

At a very basic level, user interface (UI) design is the set of pages, screens, and visual elements such as button styles, icons, that allow a user to interact with your product or service. UI is the graphical layout, the visual appearance of a product. A good design will attract people and ensure a nice product experience. UI design includes the elements that users interact with such as text, images, videos, forms, button colours, tags, text fields, drop-down lists, graphic design, checkboxes, icons, etc. and actions that will happen when user’s click, enter or drag the elements presented above.
What Is User Experience (UX) Design?

The term “UX” stands for “user experience” and it refers to the overall experience a user has while interacting with a website, app, a digital product or service. The user experience is determined by how difficult or easy a person interacts with the user interface (UI) elements. If their journey is smooth, intuitive, the navigation is logical and they get the feeling that they can accomplish their goal fast, then you are offering a good user experience. On the other hand, if your users are having difficulties in interacting with your web product, if they feel that it is clunky and confusing, then you might reconsider your UX.
While UI designers are designing how the user interface will look like, UX designers are deciding how the user interface acts.
UX professionals will determine the structure and the functionality of the website or app such as: how it is coordinated, how all parts correlate, and how everything works together.
UX design involves plenty of research on understanding customer behaviour and pain points, potential market gaps, competitor analysis. Besides, UX is in charge of considering business objectives and goals when building products to align with the company’s mission and vision.
UX Design Best Practices
The ultimate purpose of UX is to improve the end user’s interaction and understanding of the products and services as outlined by the company. For a better interpretation, we would like to present you a great visual created by Peter Morville, designer and information architect. He developed a honeycomb visual to highlight the 7 elements of user experience design.
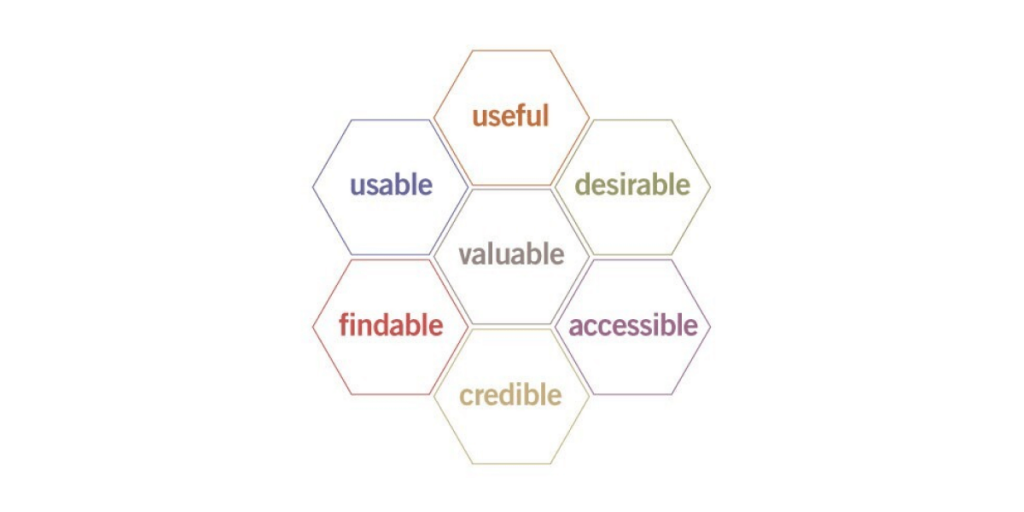 This honeycomb is the foundation of best practices in UX design and it is destined to help user experience specialists to guide their efforts in the user journey, by touching the following points:
This honeycomb is the foundation of best practices in UX design and it is destined to help user experience specialists to guide their efforts in the user journey, by touching the following points:
- The way users would discover the company’s product;
- The actions set they take as they interact with the website/app;
- The thoughts and feelings they have when they try to achieve their goal;
- The overall impression they take away from the interaction.
The purpose of UX best practices is to ensure that the product or service, web or app, is delivered exactly how users expect, meet their needs, allow them to easily achieve their goal, and increase conversions.
What are the Key Differences Between UX and UI?
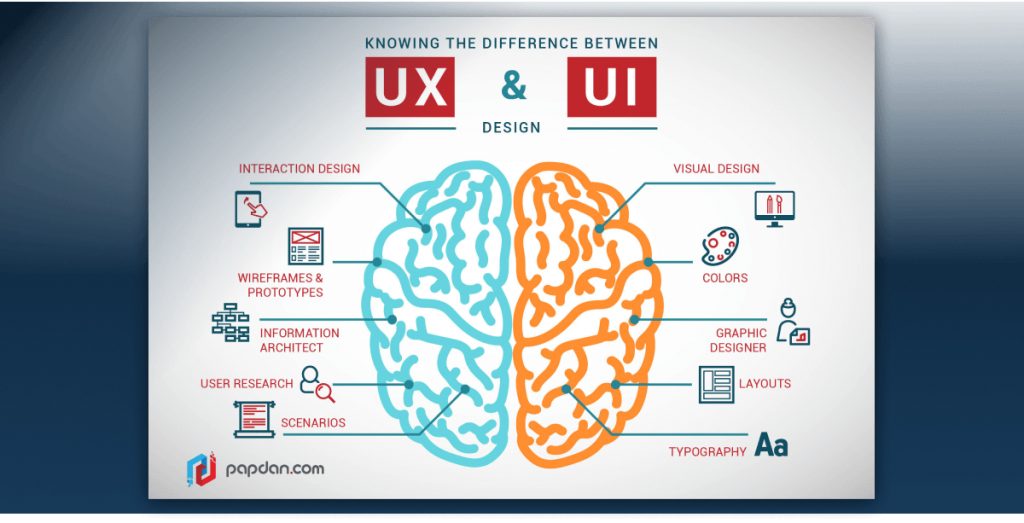
UX design and UI design are always interconnected. When thinking about their functionality, UI takes care of how things look and UX covers how things work. Even though they are interconnecting in product development, they serve distinctive roles. While UX is a process, UI is a deliverable.
We are going to dive deeper into the main key differences between them and try to clarify these concepts for you:
- Main focus – the UX and UI designers have different tasks in the prototyping phase. On conceptual aspects, UI pays more attention to the front-end interface, while UX is more oriented on the back-end. When you meet with your customers, we recommend you to present them the design made by the UI designers and when talking with the developers, show them the project made by the UX designers.
- Thinking process – UX will always have critical thinking, based on data, and creative thinking when it comes to implementing new concepts. UI will use creative thinking when designing the interface and convergent thinking when implementing it.
- Design – UX is dictated by the user’s research and needs, while UI is dictated by the client’s needs and requirements.
- Visual strengths – UX is best on task flows and scenarios, UI is best on colours and typography.
- Design focus – UX is human-centred, UI is visual design centred.
- Expertise – UX is more focused on prototypes, wireframes, and research, while UI is more focused on mockups, graphics, and layouts.
- Colours – UI designers will always use the full-colour spectrum when designing the prototype, while UX designers use only black, white, and grey in this stage. On one hand, UI designers will put a lot of effort into making the colours of the buttons as realistic as possible before clicking it and after clicking it. On the other hand, UX designers will place the button on the right place and will leave a note such as: “Grey after clicking”.
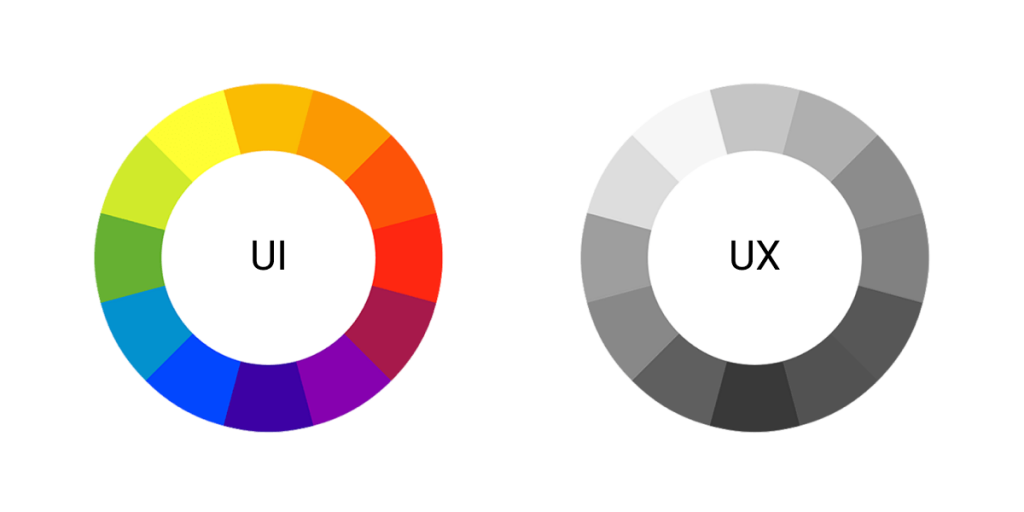
How Do UX and UI Work Together?
UX and UI are not the same, but besides their differences, they complete each other. UX design makes the interface effective, UI design makes the interface appealing. UX helps users reach their goals, UI creates emotional connections. UX and UI live in harmony and serve the same business goals. Now, we would like to show you how UX UI depend on each other to create the perfect customer experience, drive business success, increase traffic, retention, and revenue.
Research
UX is mostly based on researching the experience of a user with a product, collecting and analyzing data, using techniques such as:
- Personas – fictional user profiles that represent the target users that a product is built for; these personas profiles are created after detailed research on demographics, online behaviour, search terms, time spent on site, etc. Based on these personas, UX designers will identify the product features that would appeal the most to theoretical users.
- Journey mapping – this technique means creating a visual representation of the user’s journey with a product from the first contact to a long-term relationship with it.
- Brainstorming – after analyzing the current user experience with a product and outline the perfect experience based on feedback, UX designers start to brainstorm new ideas and methods to implement the necessary product changes. This is going to be the first step of UX design. UI designers will do the same brainstorming session when designing the interface, based on the data found by UX research.
Architecture
The next step after using the research to develop the strategy on improving customer experience, UX UI designers will start the collaboration into drafting and implementing the designs. In this stage, the UX team and the UI team will start working on the arrangement of the product’s information or content to deliver the most satisfactory experience. They will use the following methods:
- Navigation and Layout – this is the centre stage of UI because the user interface is based and informed by the navigation and layout. These will indicate the overall experience of the product. UX is the “science” and UI is the “art”.
- Wireframing – this process refers to the creation of the overall visual structure that maps out the whole look and feel of the website or app. Creating the wireframes implies the collaboration between UI and UX specialists into designing the key elements to deliver the big picture of brand experience. For UX it means designing the logos, establishing the colour pallet, and content, while UI designers will focus on page layouts such as sitemaps, snapshots, elements arrangements, screen menu, the inclusion of interactive forms, etc.
- Prototyping – this step follows the wireframing and delivers the initial model of the website or application. A basic wireframe concept is going to be built and will give the users the possibility of interacting with the sample version of your product. In this stage the UX will focus more on the general experience of the prototype model and UI will use it to test the efficiency and attractiveness of the interface design.
Testing
After all the hard work, it is time to release the finished product. A finished version of the product means an officially released version that is accessible to the public. Even though this version is public, UX and UI specialists will continue testing the product, use data, and user’s feedback to improve the product and refine the experience and interface in the next version. They will test:
- Usability – users will test the product while UX designers will observe and analyze if the product is easy and pleasant when it comes to completing a specific task.
- A/B Testing – means that users will test two versions of the product, version A and version B. Version B has a slight design variation. From this type of testing, you will gather information about which version is preferred. The indicator of user preference is the conversion rate which measures the number of visitors that complete the desired action during their visit (buying a product, subscribing to a newsletter, purchasing a membership, etc.). A/B testing will reveal which version resonates better with the target audience and which parts of the product version need improvements.
UI design and UX design are based on different skill sets, but they are like lock and key. A hard to use, or confusing interface cannot be saved by a beautiful design and a perfect, outstanding user experience will fail because of a bad visual interface design that triggers an unpleasant feeling.
Our Expertise
In a constantly evolving world, the ways to engage with your target audience have to get more advanced and demand innovation. Therefore, it is very important to consider a professional agency when it comes to custom development and web design.
We have a great experience in delivering top-notch results that both our partners and their customers are happy with.
One of our projects was focused on designing an outstandingly beautiful website that provides a seamless user experience. We started by creating a strong, creative, and technical team. Our approach was to research the industry and the types of users, so we can deliver a great user experience. On prototyping and testing phases, we focused on usability and performance to make sure that everything runs smoothly, then completed the experience with the artwork.
 You can take a look at the full case study and see for yourself that the UX UI is as important as the development of your website or app. Also, here you can find more of our projects and if you like our work, contact us. Let’s have a chat and see what’s the best way for your business to reach its true potential.
You can take a look at the full case study and see for yourself that the UX UI is as important as the development of your website or app. Also, here you can find more of our projects and if you like our work, contact us. Let’s have a chat and see what’s the best way for your business to reach its true potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Because UX and UI complete each other. The UX focuses on how the app or website works, while UI focuses on how it looks. You can have a good looking product, but if you don’t know how it works, the aesthetics are useless.
Both are equally important. It might look like the UI is more important than UX, but the truth is, UI cannot fully function without UX and vice versa.
Usually, the UX is done first and the UI second. UX makes the interface useful and UI makes it beautiful.
No, but coding gives you an advantage to understand what’s feasible and what’s not.